eHAZOP (SAFOP) STUDIES - PROVEN VEHICLE TO DELIVER VALUE ADDED & MANAGE RISK
1.0 INTRODUCTION
eHAZOP, often referred to as SAFOP or an Electrical Safety Review (ESR) , is a series of studies that can be used during the various phases of a Power Electrical Engineering Project. These studies are applied to assist in achieving objectives that include :
- Optimising the reliability, security, safety and operability of the design to best meet plant/facility objectives
- Identifying major hazards to different personnel in construction, commissioning and operation of high voltage installations
- Front End Loading (FEL) the design to avoid waste and rework and help assure compliance with budget and schedule
- Facilitate organisational learning by providing a structured process to embed prior learnings and experiences in the design
- Build JV partner, stakeholder and end user commitment to the design.
2.0 THE TYPES OF eHAZOP STUDIES INVOLVED
Our eHAZOP technology involves a number of study elements. The use and emphasis placed on a given study element depends on the client's specific eHAZOP objectives and when the study is completed within the project cycle.
| Study Name |
Study Purpose |
KEY INPUTS |
| PHILOP |
PHILOP is a tool for systematically reviewing the philosophies, reports and principles that underpin the electrical network design and assessing their adequacy and fitness for purpose. |
Philosophy Reports
Basis Of Design
System Studies/Reports
Some Equipment Specifications |
| DESIGN |
DESIGN examines standards of design and security of supply. It does not include analysis of design calculations, but rather, examines major items of plant and equipment and considers any limitations and their effect on system operability. |
Key Single Line Diagrams
Equipment Schematics
Equipment Wiring Diagrams
Equipment Layout Drawings
Some Equipment Specifications |
| INSTALLATION |
INSTALLATION examines hazards present in the construction, commissioning and operation of electrical installations and considers them in relation to safety of electrical and non electrical personnel. |
Safety Policy
Safety Procedures/Systems
Electrical Work Practices
Electrical Construction Plan
Electrical Commissioning Plan
|
| OPERATION |
OPERATION considers tasks performed by electrical operators during normal and abnormal conditions. It assesses the usability of equipment and reviews instructions necessary to prevent human error as far as is reasonably practicable. |
Emergency Procedures
Electrical Authorisation System
Electrical Training Plan
Electrical Operating Procedures
Manufacturers Instructions |
| NETOP |
NETOP considers the performance of the overall electrical network for a given set of end user operating conditions and identifies limitations and areas for improvement. It considers interactions between electrical equipment and complements DESIGN which is primarily concerned with individual items of equipment. |
Plant Operating Scenarios
Dynamic Stability Studies
(Process/Electrical)
Generator AVR Studies
Load Flow Studies
Voltage Regulation Studies
Motor Re-acceleration Studies |
Historically, eHAZOP consisted of DESIGN, OPERATION and INSTALLATION only. Today, this study combination is often referred to as eHAZOP Light.
3.0 WHEN IS AN eHAZOP REQUIRED? - EVALUATION CRITERIA
Four key objective criteria are used for evaluating the requirement to perform an eHAZOP for a given project. These are :
- The estimated magnitude of the overall electrical investment. Larger electrical investments are associated with a larger electrical footprint and a higher electrical risk profile.
- The electrical complexity of the project; eg new technology, new equipment, design innovation, complexity of system interfaces etc
- The experience and capabilities of the design team; eg knowledge of company plant/facilities/standards/operating environment, experience in designing similar plant and facilities etc
- The level of maturity of the company's safety culture and work environment
Other, more subjective criteria, may also have relevance in assessing the requirement to perform an eHAZOP. These include :
- Safety environment. The extent to which a high safety electrical awareness exists and safety is a core value in the broader business
- Electrical Stakeholder Management/Alignment - particularly relevant for Joint Venture and complex stakeholder environments
- The Regulatory environment and any specific requirements, issues or expectations
- Building end user commitment by engagement, involvement and opportunity to input
- Onboarding and demonstrably managing/discharging of company risk particularly where new Design and Construction contractors and/or many vendors/subcontractors are involved
- Developing a more structured approach to organisational learning
Challis International has developed a diagnostic based on these considerations to provide guidance in eHAZOP decision making deliberations. Please go to eHAZOP (SAFOP) DIAGNOSTIC
4.0 WHEN SHOULD AN eHAZOP BE COMPLETED?
If it is decided that an eHAZOP study is required, a choice (or choices) needs to be made about when it is best conducted within the Project cycle.
In 2005 we were involved in a study to review the benefits of eHAZOP and extract learnings about its application. We found that :
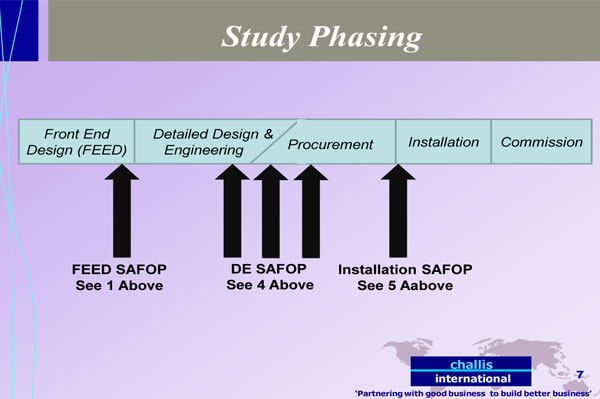
- Organizations placed particular emphasis on performing an eHAZOP at the end of the FEED stage with a view to front end loading electrical designs. Around 65% of all eHAZOP's were performed at the end of FEED. Studies undertaken at this stage emphasized PHILOP and SYSOP elements, and where appropriate, NETOP.
- For those projects where a FEED eHAZOP had been performed, around half undertook a second eHAZOP later in the project cycle.
- For those projects where no FEED eHAZOP had been performed, it was unusual for an eHAZOP to be undertaken at a later point in the project cycle.
- Around 20% of all eHAZOP studies were performed at the end of DETAILED DESIGN stage when major items of electrical equipment had been selected and key manufacturer drawings were available. Studies undertaken at this stage generally used DESIGN to look back, undertake a high level design review/QA and OPERATION and INSTALLATION to look forward and identify activities required to ensure equipment could be operated effectively (OPERATION) and key principles and tasks to be build into the construction and commissioning plan (INSTALLATION).
- Around 15% of all eHAZOP studies were performed at the start of the installation (or construction) stage when installation and commissioning plans had been prepared. Studies undertaken at this stage generally focused heavily on INSTALLATION and rigorously reviewed the activity sequences and hazards in construction, commissioning and start up with a view to identifying and mitigating risks. Some studies undertook quantifiable (probability/impact) risk assessments to help with this task
5.0 THE eHAZOP PROCESS
Irrespective of when an eHAZOP is to be performed, a number of key phases are involved. These are :
Phase 1
Scoping & Planning |
Clarification of study objectives,
Identification of study focus areas,
Agreeing Deliverables (Report Table Of Contents)
Clarifying roles/participants and venue
Preparation of an overall timetable |
| Phase 2 |
Workshop Preparation Preparation of documentation
Preparation of any workshop presentation materials
Preparation of participant packs
Software set up (nodes, promptwords/guidewords etc)
Participant/stakeholder sensing (if required),
Venue liaison |
Phase 3
Workshop Execution |
Workshop Facilitation and Worksheet Preparation |
Phase 4
Worksheets Review |
Sponsor and participant review of worksheets |
Phase 5
Draft Report Preparation |
Preparation and issue of First Draft Report as per agreed Table Of Contents and incorporating participant worksheet feedback |
Phase 6
Final Report and Study Close Out |
Preparation and issue of Second Draft Report (if required), review by client and iss |
| 
